How will Ms. Begay know if her lesson plans are effective and her students are learning?
Page 11: Implementing the Instructional Cycle
 It is critical that teachers determine beforehand what they expect students to have learned by the end of a lesson. An inexperienced teacher might begin this process by first creating lesson plans and developing activities. This kind of instruction, however, is likely to be ineffective and lack focus because the teacher has not first decided how to assess whether students have mastered a set of intended learning outcomes. By contrast, an experienced teacher will have a clear picture in his or her mind of the students’ intended learning outcomes, and will design appropriate and effective instructional activities to guide students toward mastery of those outcomes.
It is critical that teachers determine beforehand what they expect students to have learned by the end of a lesson. An inexperienced teacher might begin this process by first creating lesson plans and developing activities. This kind of instruction, however, is likely to be ineffective and lack focus because the teacher has not first decided how to assess whether students have mastered a set of intended learning outcomes. By contrast, an experienced teacher will have a clear picture in his or her mind of the students’ intended learning outcomes, and will design appropriate and effective instructional activities to guide students toward mastery of those outcomes.
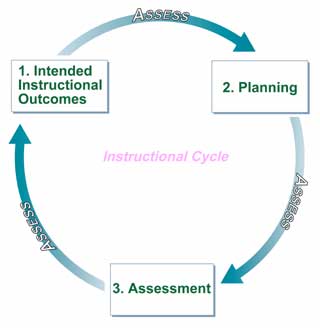
A new teacher, Ms. Begay wants to ensure that the instruction she provides will serve to promote mastery of the intended learning outcomes. She decides to use an instructional cycle to help her design effective instruction. This instructional cycle consists of three stages.
These three items comprise the instructional cycle stages.
Stage 1: Intended Instructional Outcomes
Effective teachers begin the instructional cycle by identifying the content standards and benchmarks that the lesson or unit will address. Next, the content standards are translated into measurable learning outcomes. At this stage of the instructional cycle, the teacher has a clear idea of what students need to know, understand, and be able to do to meet the standards-based curriculum. It is important for teachers to keep in mind how they will assess the intended learning outcomes.
Stage 2: Planning
In the second stage, teachers should plan effective teaching strategies and instructional activities. It is also important that teachers plan on-going formal (e.g., standardized tests) and informal (e.g., teacher-made tests, portfolios) assessments to determine students’ progress. Once the learning outcomes, instruction, and assessment have been planned, the teacher will carry out the planned instruction.
Stage 3: Assessment
In this third stage, teachers actually implement their planned assessments to determine whether students have met the intended learning outcomes. It is important to understand that assessment is not something that occurs only at the end of the instructional cycle. Assessment is planned when the intended outcomes are conceptualized and implemented during instruction and at the end of instruction to determine whether students have mastered the intended learning outcomes.
Keep in Mind
Reflective teachers use what they have learned about student performance from assessments to continually inform the instructional cycle process.